- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Jan . 15, 2025 01:36
Back to list
زجاج موصل لإيتو
Electroconductive glass, often referred to by its constituents such as إيتو or ITO (Indium Tin Oxide), is an innovative material transforming multiple industries by seamlessly merging transparency with conductivity. This capability unlocks a realm of possibilities, pivotal in enhancing modern technology applications.
Governments and global standards organizations endorse electroconductive glass due to its potential to support sustainable development goals. Its manufacturing, though complex, adheres to environmentally conscious methods, minimizing emissions and resource usage. Research continues to improve the recycling potential of these glasses, ensuring they contribute to a circular economy. As the demand for smarter, more sustainable technology grows, manufacturers and developers need reliable, authoritative sources to guide them on integrating electroconductive glass into their products. Businesses adopting this technology must rely on skilled professionals who combine expertise in materials science with practical experience in product development. Choosing electroconductive glass not only involves its immediate benefits—it’s about understanding long-term implications on product life cycle, sustainability, and consumer satisfaction. By working with certified suppliers who adhere to these standards, businesses can ensure they are delivering products that reflect cutting-edge innovation while maintaining ethical production standards. In terms of consumer electronics, transparency and touch responsiveness are increasingly pivotal features for next-generation devices. Electroconductive glass ensures these functionalities operate at optimal levels while also offering potential for future developments, such as flexible and foldable screens—a frontier not far from commercial realization. In conclusion, electroconductive glass is at the intersection of transparency and conductivity, making it indispensable in today's technology-driven world. Its applications across various sectors only underscore its versatility and importance. Leveraging this material strategically in product designs not only provides immediate technological and economic benefits but also aligns with broader environmental and social responsibilities, paving the way for innovative solutions in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
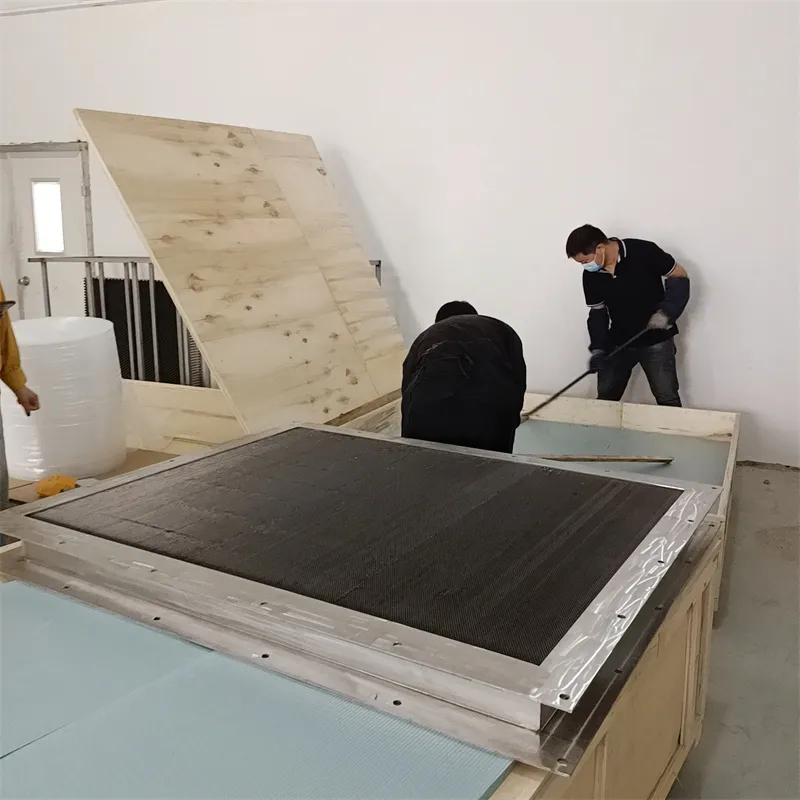

Governments and global standards organizations endorse electroconductive glass due to its potential to support sustainable development goals. Its manufacturing, though complex, adheres to environmentally conscious methods, minimizing emissions and resource usage. Research continues to improve the recycling potential of these glasses, ensuring they contribute to a circular economy. As the demand for smarter, more sustainable technology grows, manufacturers and developers need reliable, authoritative sources to guide them on integrating electroconductive glass into their products. Businesses adopting this technology must rely on skilled professionals who combine expertise in materials science with practical experience in product development. Choosing electroconductive glass not only involves its immediate benefits—it’s about understanding long-term implications on product life cycle, sustainability, and consumer satisfaction. By working with certified suppliers who adhere to these standards, businesses can ensure they are delivering products that reflect cutting-edge innovation while maintaining ethical production standards. In terms of consumer electronics, transparency and touch responsiveness are increasingly pivotal features for next-generation devices. Electroconductive glass ensures these functionalities operate at optimal levels while also offering potential for future developments, such as flexible and foldable screens—a frontier not far from commercial realization. In conclusion, electroconductive glass is at the intersection of transparency and conductivity, making it indispensable in today's technology-driven world. Its applications across various sectors only underscore its versatility and importance. Leveraging this material strategically in product designs not only provides immediate technological and economic benefits but also aligns with broader environmental and social responsibilities, paving the way for innovative solutions in a rapidly evolving technological landscape.
Prev:
Next:
Products categories
Latest news
-
Why Vented Aluminum Honeycomb Is Leading the Way in Shielding and Ventilation SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Stainless Steel Honeycomb Panel is the Ultimate Choice for High-Tech Shielding and ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Honeycomb Strips Are Revolutionizing High-Speed Sealing SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Shielded Glass Innovation Powers the Future of Electromagnetic ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Precision Starts Here: Revolutionizing Airflow Control with Honeycomb Wind Tunnel SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Elevate Industrial Performance with Precision-Engineered Steel Honeycomb Core SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Vented Aluminum Honeycomb: A Smart Shield for Airflow and EMI ControlNewsJul.11,2025















