- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
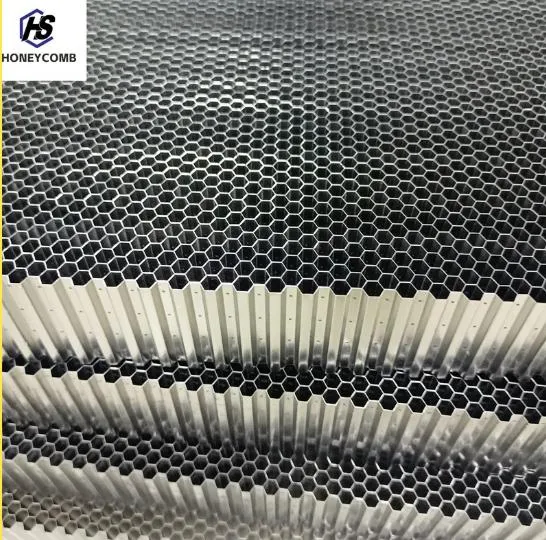
Elevate Industrial Performance with Precision-Engineered Steel Honeycomb Core Solutions
When it comes to structural reinforcement, airflow control, and lightweight durability, few materials perform with the consistency and strength of the steel honeycomb core. Engineered for high-end industrial, aerospace, and energy sectors, this next-generation solution combines advanced metallurgy with a high-precision design structure. Manufactured using premium stainless steel grades and perfected production techniques, the steel honeycomb core has become a vital component in everything from honeycomb sandwich panels to flow rectifiers.

Comparing 304 and 316L in Steel Honeycomb Core Applications
Not all stainless steel is created equal. For the steel honeycomb core, material selection plays a crucial role in durability, corrosion resistance, and environmental adaptability. The two most widely used grades in manufacturing are 304 and 316L stainless steel, each bringing unique advantages to specific applications.
Grade 304 offers excellent strength and workability, making it ideal for general-purpose steel honeycomb core structures used in interior components or environments with limited exposure to corrosive agents. On the other hand, 316L provides enhanced corrosion resistance due to its molybdenum content, making it the preferred choice in marine, chemical, and outdoor applications where moisture or corrosive vapors are prevalent.
By offering both materials, manufacturers can tailor steel honeycomb core solutions based on the mechanical demands and environmental exposures of each project. This versatility has made steel honeycombs indispensable in industries such as aerospace interiors, energy infrastructure, and automotive design.
Manufacturing Methods of Steel Honeycomb Core Panels
The quality and reliability of the steel honeycomb core depend significantly on how it is manufactured. Two of the most widely used production techniques are expansion and corrugation, each offering different advantages in structural integrity and cost-effectiveness.
In the expansion method, precision-cut sheets of stainless steel are adhesively bonded or spot welded and then expanded into their honeycomb form. This method is particularly effective for lightweight, large-format applications such as aircraft flooring or wall reinforcements.
The corrugation method, meanwhile, involves shaping individual steel strips into a corrugated pattern and then bonding them into a steel honeycomb sheet. This results in even higher compressive strength and is often used where additional structural reinforcement is required.
Advanced laser welding techniques are also increasingly used to enhance the mechanical reliability and minimize the heat-affected zone in the steel honeycomb core. These methods ensure high flatness, precision cell geometry, and exceptional load-bearing capacity—all while maintaining lightweight characteristics.
Steel Honeycomb Core in Airflow Rectifier Systems
One of the most promising and high-precision applications of the steel honeycomb core is in airflow rectifier systems. These systems are essential in wind tunnels, HVAC units, and energy research labs, where controlling turbulence and directional flow is critical.
Thanks to its geometric uniformity and rigidity, the steel honeycomb sheet serves as an ideal flow straightening medium. Air entering a turbulent system is channeled through the narrow cells of the honeycomb, effectively eliminating lateral velocity components and producing a steady, laminar output.
Unlike traditional plastic or aluminum rectifiers, the steel honeycomb core can withstand high temperatures and pressures without deformation. This makes it particularly well-suited for industrial and military wind tunnels or cleanrooms where airflow accuracy is essential.
Moreover, its stainless steel composition ensures that it remains corrosion-resistant even in chemically active or moisture-laden environments, providing a longer operational life with minimal maintenance.
Expanding Use of Honeycomb Sandwich Panel Structures
The combination of steel honeycomb core with various facing materials results in the high-strength, lightweight solution known as the honeycomb sandwich panel. These panels are redefining structural design across transportation, architecture, and defense sectors.
In transportation, honeycomb sandwich panels are increasingly being used in the construction of train interiors, ship bulkheads, and aerospace partitions due to their incredible strength-to-weight ratio. In architecture, they allow for visually striking yet structurally sound facades, especially in high-rise buildings and industrial installations.
The inner steel honeycomb core provides stiffness and compressive strength, while the outer sheets (typically aluminum, stainless steel, or composite) add impact resistance and surface finish. This makes honeycomb sandwich panels the go-to choice for designers seeking material efficiency without compromising durability or aesthetic appeal.
Custom panel designs can incorporate fire-resistant coatings, acoustic insulation layers, and even decorative surfaces, making them as functional as they are versatile. With unmatched thermal stability and mechanical consistency, honeycomb sandwich panels deliver both form and function at a premium level.
Steel Honeycomb Core FAQs
What is the purpose of using a steel honeycomb core?
The steel honeycomb core offers high strength, lightweight structure, and excellent load-bearing capacity. It is widely used in industrial, architectural, and aerospace applications requiring structural reinforcement or flow control.
What are the benefits of using 316L over 304 in steel honeycomb core production?
316L offers enhanced corrosion resistance due to its molybdenum content, making it suitable for marine and chemical environments. 304 is more cost-effective and sufficient for less corrosive settings, both being popular for steel honeycomb core systems.
How are steel honeycomb sheets manufactured?
Steel honeycomb sheets are produced through expansion or corrugation processes. These involve shaping or stretching bonded steel strips into uniform honeycomb cells, followed by precision welding or bonding to create strong, lightweight structures.
Where are honeycomb sandwich panels typically used?
Honeycomb sandwich panels are commonly used in aircraft cabins, train interiors, building facades, and ship partitions. Their strength-to-weight ratio and fire-resistant features make them ideal for both structural and aesthetic applications.
Can steel honeycomb core be used in airflow rectifiers?
Yes, the steel honeycomb core is highly effective in airflow rectifiers due to its ability to streamline turbulent air into laminar flow. Its rigidity and temperature resistance make it ideal for use in wind tunnels and industrial HVAC systems.
Products categories
-
Why Vented Aluminum Honeycomb Is Leading the Way in Shielding and Ventilation SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Stainless Steel Honeycomb Panel is the Ultimate Choice for High-Tech Shielding and ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Honeycomb Strips Are Revolutionizing High-Speed Sealing SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Shielded Glass Innovation Powers the Future of Electromagnetic ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Precision Starts Here: Revolutionizing Airflow Control with Honeycomb Wind Tunnel SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Vented Aluminum Honeycomb: A Smart Shield for Airflow and EMI ControlNewsJul.11,2025
-
Steel Honeycomb Core: The Backbone of Structural ExcellenceNewsJul.11,2025















