- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Jan . 31, 2025 01:50
Back to list
saídas de ar com guia de ondas blindado emi rfi
Air vents equipped with EMI/RFI shielded waveguides have become a pivotal component in high-tech environments where electronic equipment is densely packed, and electromagnetic interference can cause significant disruptions. Understanding the complex dynamics of these specialized vents is crucial for organizations keen on maintaining reliable and efficient electronic operations.
2. Frequency Range Different applications demand various frequency blocking capabilities. High-frequency signals require differently structured waveguides compared to low-frequency ones. Attention to the specific interference challenges faced by the equipment is paramount in selecting the appropriate vent specification. 3. Regulatory Compliance Devices that integrate waveguide technology must comply with international standards. Recognized organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), provide guidelines ensuring these vents meet stringent EMI/RFI mitigation requirements. Adherence to these standards not only guarantees performance but also positions a product as trustworthy in the market. 4. Installation and Maintenance Incorporating air vents with waveguides involves precise alignment and secure fastening to prevent gaps that could diminish their shielding effectiveness. Regular maintenance checks ensure vents remain unobstructed and perform as intended over time. A practical insight into these devices can be drawn from their application in data centers. In these environments, equipment is densely packed, and the prevalence of high-frequency operations makes them susceptible to interference. Here, shielded waveguide air vents ensure reliable data throughput by protecting servers from external and internal EMI/RFI sources. Furthermore, the propulsion of 5G technology and its infrastructure development presents new challenges and opportunities for waveguide technology. The increasing data rates and higher frequency bands necessitate advanced shielding solutions to prevent interference and maintain the integrity of communication lines. In conclusion, EMI/RFI shielded air vents with waveguides embody a balanced blend of traditional thermal management and advanced electromagnetic protection. These devices are indispensable in settings where maintaining signal quality is a non-negotiable priority. By selecting the right combination of material, frequency range, and maintaining adherence to compliance standards, organizations can ensure their electronic environments are both efficient and secure. Such strategic decisions not only enhance performance but also reinforce the trust organizations place in their technological investments.
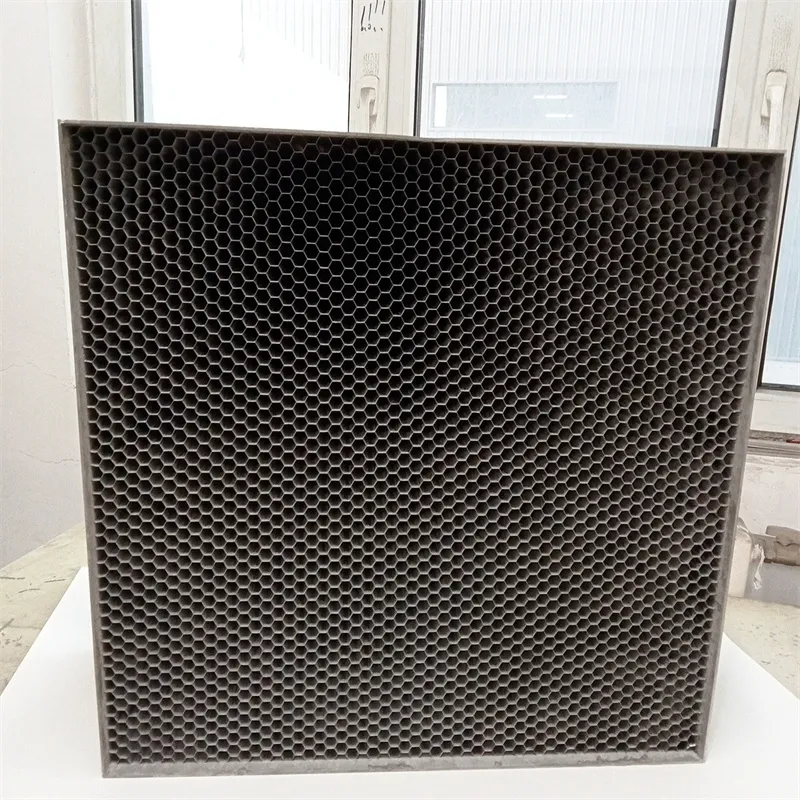


2. Frequency Range Different applications demand various frequency blocking capabilities. High-frequency signals require differently structured waveguides compared to low-frequency ones. Attention to the specific interference challenges faced by the equipment is paramount in selecting the appropriate vent specification. 3. Regulatory Compliance Devices that integrate waveguide technology must comply with international standards. Recognized organizations, such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), provide guidelines ensuring these vents meet stringent EMI/RFI mitigation requirements. Adherence to these standards not only guarantees performance but also positions a product as trustworthy in the market. 4. Installation and Maintenance Incorporating air vents with waveguides involves precise alignment and secure fastening to prevent gaps that could diminish their shielding effectiveness. Regular maintenance checks ensure vents remain unobstructed and perform as intended over time. A practical insight into these devices can be drawn from their application in data centers. In these environments, equipment is densely packed, and the prevalence of high-frequency operations makes them susceptible to interference. Here, shielded waveguide air vents ensure reliable data throughput by protecting servers from external and internal EMI/RFI sources. Furthermore, the propulsion of 5G technology and its infrastructure development presents new challenges and opportunities for waveguide technology. The increasing data rates and higher frequency bands necessitate advanced shielding solutions to prevent interference and maintain the integrity of communication lines. In conclusion, EMI/RFI shielded air vents with waveguides embody a balanced blend of traditional thermal management and advanced electromagnetic protection. These devices are indispensable in settings where maintaining signal quality is a non-negotiable priority. By selecting the right combination of material, frequency range, and maintaining adherence to compliance standards, organizations can ensure their electronic environments are both efficient and secure. Such strategic decisions not only enhance performance but also reinforce the trust organizations place in their technological investments.
Prev:
Next:
Products categories
Latest news
-
Why Vented Aluminum Honeycomb Is Leading the Way in Shielding and Ventilation SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Stainless Steel Honeycomb Panel is the Ultimate Choice for High-Tech Shielding and ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Honeycomb Strips Are Revolutionizing High-Speed Sealing SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Shielded Glass Innovation Powers the Future of Electromagnetic ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Precision Starts Here: Revolutionizing Airflow Control with Honeycomb Wind Tunnel SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Elevate Industrial Performance with Precision-Engineered Steel Honeycomb Core SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Vented Aluminum Honeycomb: A Smart Shield for Airflow and EMI ControlNewsJul.11,2025















