- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Jan . 29, 2025 01:42
Back to list
ventilación de panales
Ventilation is crucial for maintaining the efficiency and longevity of beehives. Ensuring proper ventilation in beehives not only supports the health and productivity of bees but also enhances the quality of honey and wax produced. This article delves into the expert techniques and authoritative insights on optimal beehive ventilation, highlighting its significance and practical applications for beekeepers.
Authoritative recommendations from entomologists and experienced beekeepers underscore the critical role of adjusting hive ventilation according to seasonal changes. For instance, during the winter, overly ventilated hives can lead to heat loss and energy drain for bee colonies. Beekeepers are advised to reduce the size of hive entrances and add insulating materials to maintain a balance between adequate ventilation and warmth. Conversely, during the summer, increasing ventilation aids in cooling the hive and preventing the build-up of harmful pathogens that thrive in warm, stagnant environments. Trustworthiness in beehive management emerges from transparency and continual learning. Successful beekeepers often engage in regular hive inspections to monitor ventilation effectiveness, tweaking their approaches based on observed results. Furthermore, sharing genuine experiences and outcomes with the beekeeping community fosters a culture of reliability and support. Collaboration with research institutions and participation in beekeeping forums can also enhance one's knowledge and practices, ensuring that ventilatory strategies are both innovative and grounded in scientific research. In conclusion, the importance of proper hive ventilation is paramount in sustaining healthy and productive bee colonies. By integrating experience, expertise, authoritative strategies, and trustworthiness into ventilation practices, beekeepers not only optimize the conditions within their hives but also contribute to the overall well-being of the bee population and ultimately, their own success. Whether through modifications like screened bottoms or the judicious adjustment of hive entrances, effective ventilation is a critical component of modern apiculture that nurtures thriving colonies and high-quality honey production.
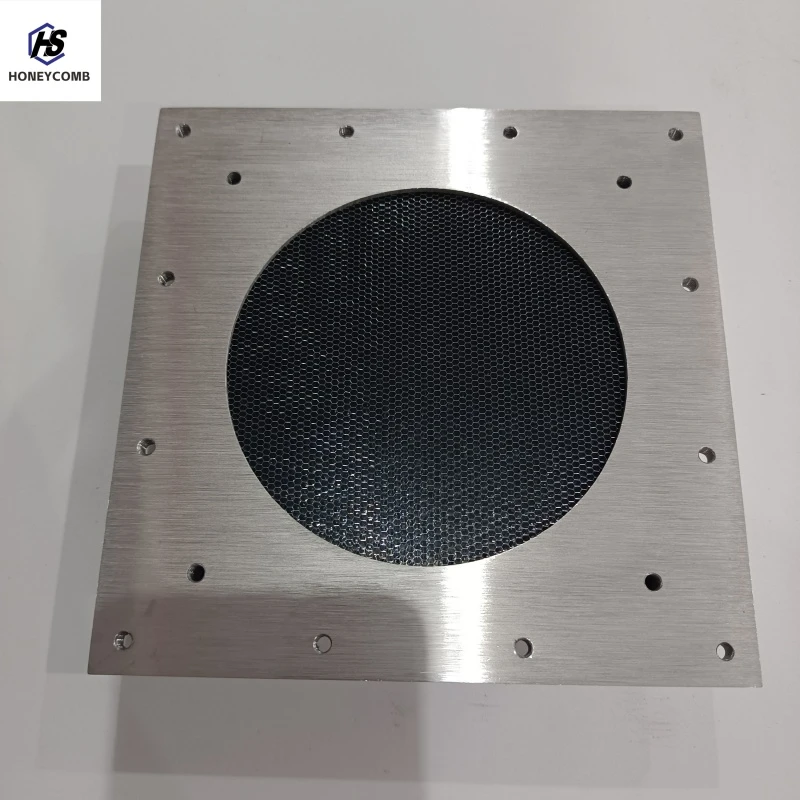

Authoritative recommendations from entomologists and experienced beekeepers underscore the critical role of adjusting hive ventilation according to seasonal changes. For instance, during the winter, overly ventilated hives can lead to heat loss and energy drain for bee colonies. Beekeepers are advised to reduce the size of hive entrances and add insulating materials to maintain a balance between adequate ventilation and warmth. Conversely, during the summer, increasing ventilation aids in cooling the hive and preventing the build-up of harmful pathogens that thrive in warm, stagnant environments. Trustworthiness in beehive management emerges from transparency and continual learning. Successful beekeepers often engage in regular hive inspections to monitor ventilation effectiveness, tweaking their approaches based on observed results. Furthermore, sharing genuine experiences and outcomes with the beekeeping community fosters a culture of reliability and support. Collaboration with research institutions and participation in beekeeping forums can also enhance one's knowledge and practices, ensuring that ventilatory strategies are both innovative and grounded in scientific research. In conclusion, the importance of proper hive ventilation is paramount in sustaining healthy and productive bee colonies. By integrating experience, expertise, authoritative strategies, and trustworthiness into ventilation practices, beekeepers not only optimize the conditions within their hives but also contribute to the overall well-being of the bee population and ultimately, their own success. Whether through modifications like screened bottoms or the judicious adjustment of hive entrances, effective ventilation is a critical component of modern apiculture that nurtures thriving colonies and high-quality honey production.
Next:
Products categories
Latest news
-
Why Vented Aluminum Honeycomb Is Leading the Way in Shielding and Ventilation SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Stainless Steel Honeycomb Panel is the Ultimate Choice for High-Tech Shielding and ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Honeycomb Strips Are Revolutionizing High-Speed Sealing SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Shielded Glass Innovation Powers the Future of Electromagnetic ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Precision Starts Here: Revolutionizing Airflow Control with Honeycomb Wind Tunnel SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Elevate Industrial Performance with Precision-Engineered Steel Honeycomb Core SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Vented Aluminum Honeycomb: A Smart Shield for Airflow and EMI ControlNewsJul.11,2025















