- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Jan . 14, 2025 10:27
Back to list
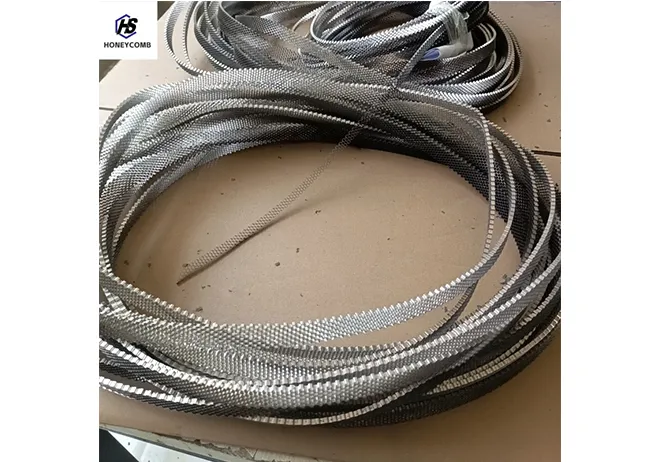
20mm Core Size Stainless Steel Honeycomb Core Panel - Customized for Wind Tunnel Applications
Conductive ITO glass, an indispensable component in the modern electronics realm, is taking strides as a key player in technology development. It stands out not just for its technical prowess but also for the revolutionary ways it integrates into our daily tech experiences. This article delves into the nuances of Indium Tin Oxide (ITO) conductive glass, examining its real-world applications, expert insights, authority it commands in the tech industry, and trustworthiness for consumers and professionals alike.
Trustworthiness is critical when considering materials in manufacturing conductive surfaces. ITO glass is widely trusted due to its proven track record of consistency and reliability. Its resilience under various environmental conditions—such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to sunlight—has been thoroughly vetted by manufacturers and third-party testing bodies alike. These factors instill confidence among OEMs and end-users, reinforcing its role as a dependable standard in electronics. To leverage the potential of ITO conductive glass in product design, companies must prioritize sustainability and recyclability. Given indium's limited availability, the industry faces pressures to innovate alternative recycling methods that ensure prolonged usage without depleting natural reserves. This commitment not only exemplifies environmental stewardship but also aligns with evolving corporate and consumer sustainability goals. Moreover, as innovations continue in printed electronics and thin-film transistor technologies, ITO glass will likely intersect with cutting-edge advancements. Engineers specializing in semiconductor functionality recognize the potential of ITO in minimizing energy losses, thus pushing it closer to becoming a cornerstone in future tech developments. The transition towards more flexible, thinner, and energy-efficient devices is an exciting frontier, with ITO at its core. In conclusion, the world of conductive ITO glass is rapidly evolving, driven by expert insights and advancements that solidify its authority in the industry. Its proven effectiveness and potential expansions into novel applications make it an exciting candidate for future technological innovations. With heightened awareness and market demands, stakeholders, from manufacturers to end-users, acknowledge and trust ITO glass as a reliable, efficient choice to power the next wave of electronic devices.


Trustworthiness is critical when considering materials in manufacturing conductive surfaces. ITO glass is widely trusted due to its proven track record of consistency and reliability. Its resilience under various environmental conditions—such as temperature fluctuations and exposure to sunlight—has been thoroughly vetted by manufacturers and third-party testing bodies alike. These factors instill confidence among OEMs and end-users, reinforcing its role as a dependable standard in electronics. To leverage the potential of ITO conductive glass in product design, companies must prioritize sustainability and recyclability. Given indium's limited availability, the industry faces pressures to innovate alternative recycling methods that ensure prolonged usage without depleting natural reserves. This commitment not only exemplifies environmental stewardship but also aligns with evolving corporate and consumer sustainability goals. Moreover, as innovations continue in printed electronics and thin-film transistor technologies, ITO glass will likely intersect with cutting-edge advancements. Engineers specializing in semiconductor functionality recognize the potential of ITO in minimizing energy losses, thus pushing it closer to becoming a cornerstone in future tech developments. The transition towards more flexible, thinner, and energy-efficient devices is an exciting frontier, with ITO at its core. In conclusion, the world of conductive ITO glass is rapidly evolving, driven by expert insights and advancements that solidify its authority in the industry. Its proven effectiveness and potential expansions into novel applications make it an exciting candidate for future technological innovations. With heightened awareness and market demands, stakeholders, from manufacturers to end-users, acknowledge and trust ITO glass as a reliable, efficient choice to power the next wave of electronic devices.
Next:
Products categories
Latest news
-
Why Vented Aluminum Honeycomb Is Leading the Way in Shielding and Ventilation SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Stainless Steel Honeycomb Panel is the Ultimate Choice for High-Tech Shielding and ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Honeycomb Strips Are Revolutionizing High-Speed Sealing SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Shielded Glass Innovation Powers the Future of Electromagnetic ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Precision Starts Here: Revolutionizing Airflow Control with Honeycomb Wind Tunnel SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Elevate Industrial Performance with Precision-Engineered Steel Honeycomb Core SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Vented Aluminum Honeycomb: A Smart Shield for Airflow and EMI ControlNewsJul.11,2025















