- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Azerbaijani
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Bulgarian
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- China
- China (Taiwan)
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Finnish
- French
- Frisian
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Greek
- Gujarati
- Haitian Creole
- hausa
- hawaiian
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Miao
- Indonesian
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Malay
- Persian
- Portuguese
- Punjabi
- Russian
- Spanish
- Swahili
- Telugu
- Vietnamese
Feb . 11, 2025 11:36
Back to list
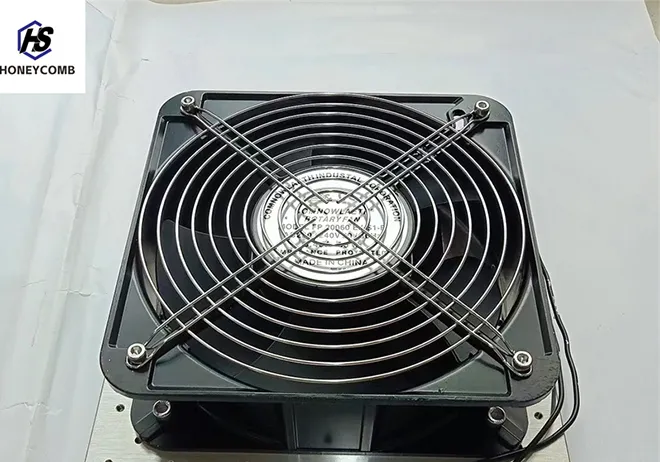
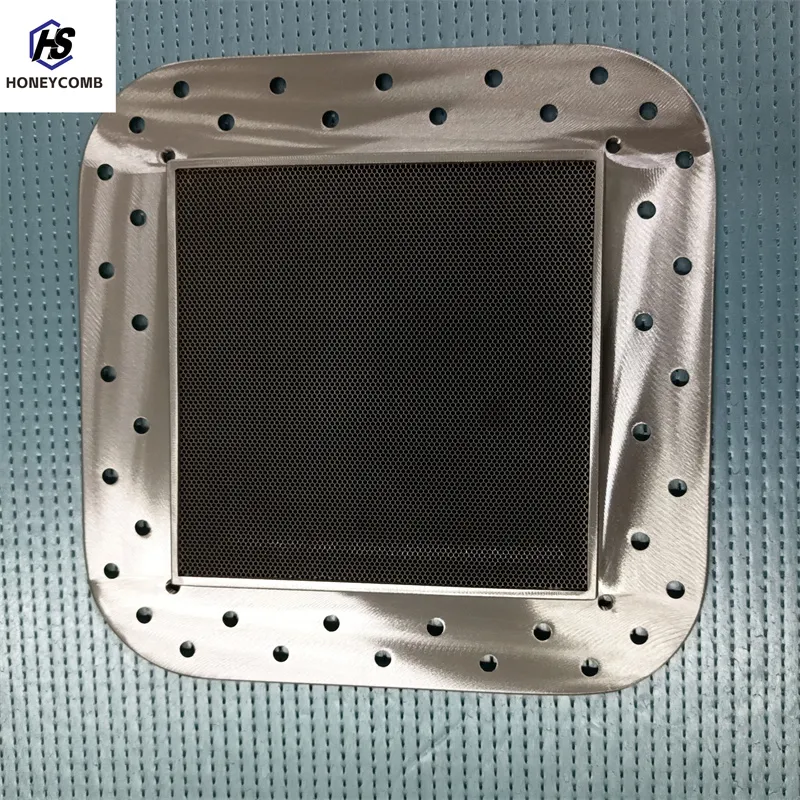
nido d'ape in alluminio estruso
Aluminum extruded honeycomb structures have revolutionized multiple industrial sectors with their unique combination of strength, flexibility, and lightweight characteristics. As a recognized expert in the field, let’s delve into the attributes that make these structures indispensable across various applications, focusing on their experiential and authoritative usage.
In the automotive realm, the integration of nido d'ape aluminum has opened avenues for innovation in design and functionality. The lightweight nature of these materials aids in reducing the vehicle’s weight, thereby enhancing acceleration, fuel economy, and handling qualities. Additionally, they increase the vehicle's structural integrity and impact resistance, reinforcing safety protocols while augmenting driving performance. This balance between safety and efficiency embodies the expertise-driven approach that automotive engineers strive for. Construction has also benefitted significantly from the advent of extruded aluminum honeycomb structures. Being resistant to moisture and temperature fluctuations, they are ideal for cladding and flooring in both commercial and residential buildings. The structures possess a unique capacity to distribute stress evenly, mitigating potential environmental impacts over extended periods. Consequently, architects and builders not only save on repair and maintenance costs but also contribute positively to the sustainability index of their projects. Trust in these materials comes not only from their empirical performance metrics but also from authoritative testing and endorsements by industry standards organizations. Renowned associations have constantly validated the efficacy of aluminum honeycombs through rigorous testing and certification, reinforcing their reputation as reliable and trustworthy materials. As industries become increasingly competitive and demand economic and sustainable solutions, aluminum extruded honeycomb structures stand out as a pivotal resource. They offer not just exceptional physical properties, but also limitless potential for innovation, corroborated by years of practical research and authoritative affirmation. The experience across varied applications highlights its transformative capacity, establishing it as a cornerstone in modern engineering and design disciplines. Such a robust yet lightweight solution is a testament to the progressive trajectory of materials science, evidencing aluminum’s reinvention in a world ever-evolving towards efficiency and sustainability.

In the automotive realm, the integration of nido d'ape aluminum has opened avenues for innovation in design and functionality. The lightweight nature of these materials aids in reducing the vehicle’s weight, thereby enhancing acceleration, fuel economy, and handling qualities. Additionally, they increase the vehicle's structural integrity and impact resistance, reinforcing safety protocols while augmenting driving performance. This balance between safety and efficiency embodies the expertise-driven approach that automotive engineers strive for. Construction has also benefitted significantly from the advent of extruded aluminum honeycomb structures. Being resistant to moisture and temperature fluctuations, they are ideal for cladding and flooring in both commercial and residential buildings. The structures possess a unique capacity to distribute stress evenly, mitigating potential environmental impacts over extended periods. Consequently, architects and builders not only save on repair and maintenance costs but also contribute positively to the sustainability index of their projects. Trust in these materials comes not only from their empirical performance metrics but also from authoritative testing and endorsements by industry standards organizations. Renowned associations have constantly validated the efficacy of aluminum honeycombs through rigorous testing and certification, reinforcing their reputation as reliable and trustworthy materials. As industries become increasingly competitive and demand economic and sustainable solutions, aluminum extruded honeycomb structures stand out as a pivotal resource. They offer not just exceptional physical properties, but also limitless potential for innovation, corroborated by years of practical research and authoritative affirmation. The experience across varied applications highlights its transformative capacity, establishing it as a cornerstone in modern engineering and design disciplines. Such a robust yet lightweight solution is a testament to the progressive trajectory of materials science, evidencing aluminum’s reinvention in a world ever-evolving towards efficiency and sustainability.
Prev:
Products categories
Latest news
-
Why Vented Aluminum Honeycomb Is Leading the Way in Shielding and Ventilation SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Stainless Steel Honeycomb Panel is the Ultimate Choice for High-Tech Shielding and ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Why Honeycomb Strips Are Revolutionizing High-Speed Sealing SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Shielded Glass Innovation Powers the Future of Electromagnetic ProtectionNewsJul.18,2025
-
Precision Starts Here: Revolutionizing Airflow Control with Honeycomb Wind Tunnel SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Elevate Industrial Performance with Precision-Engineered Steel Honeycomb Core SolutionsNewsJul.18,2025
-
Vented Aluminum Honeycomb: A Smart Shield for Airflow and EMI ControlNewsJul.11,2025















